荷兰招聘
在本地或远程招聘之前,了解荷兰劳动法、成本和合规要素。
了解更多
如何通过签证担保在欧洲找到工作
探索签证选择、雇主期望和提示,以提高您在欧洲获得赞助工作的机会。
了解更多
_09.jpg)
_06.jpg)
_15.jpg)
_13.jpg)
_18.jpg)
_19.jpg)
_23.jpg)
_22.jpg)
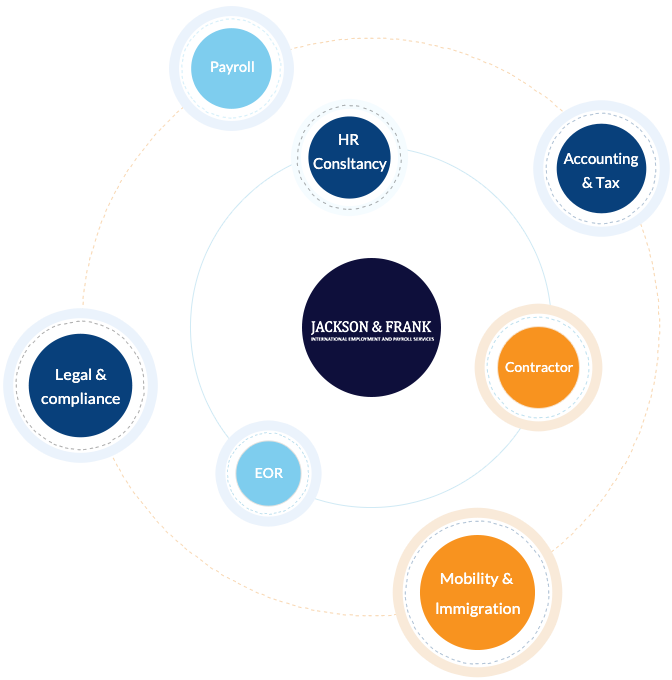
在 Jackson & Frank,我们不仅是服务提供商,更是您拓展国际业务过程中值得信赖的战略伙伴。我们的使命是简化并提升您的全球人力资源战略,帮助您自信而高效地在多个国家组建并管理卓越团队。
我们提供的服务包括:
为什么选择我们?
在 Jackson & Frank,我们不仅仅是服务提供者,更是帮助您业务在全球舞台上蓬勃发展的合作伙伴。让我们为您解决国际人力资源管理的复杂事务,您可以专注于最擅长的事情:发展您的业务。

在西班牙,主要有两种类型的劳动合同。
固定期限劳动合同是在特定期限内有效的临时雇佣协议,通常用于特定项目、季节性工作或替代缺岗员工的情况。
如果出现以下任一情形,固定期限劳动合同将自动转为无固定期限(永久)劳动合同:
永久合同:该合同为无固定期限合同。永久雇佣合同是西班牙最常见的雇佣协议类型,确立了无固定终止日期的雇佣关系,意味着雇佣关系将持续进行,直到一方终止。这种合同为雇主和员工双方提供了稳定性和保障。
在上述两种合同类型中,雇佣协议中应明确以下要点:
公共假日:
|
元旦:1月1日,星期三 |
主显节:1月6日,星期一 |
|
耶稣受难日:4月18日,星期五 |
o 劳动节:5月1日,星期四 |
|
o 圣母升天节:8月15日,星期五 o 万圣节:11月1日,星期六 o 圣母无染原罪瞻礼:12月8日,星期一 |
o 西班牙国庆节:10月12日,星期日 o 宪法日:12月6日,星期六 o 圣诞节:12月25日,星期四 |
西班牙的部分地区可能还有适用于本地的额外节假日。
耶稣受难日和复活节星期一的日期每年可能会根据农历有所变动。
年假:
在西班牙,对于每周工作40小时的员工,法定最低带薪年假为每年22个工作日。然而,具体天数可能因以下因素而有所不同:
病假:
在西班牙,当员工因疾病或受伤无法工作时,通常有权享受带薪病假。病假的具体规定可能因员工的个人情况、所属行业以及适用的集体谈判协议而有所不同。
产假:
产假是给予女性员工的一段休息时间,用于分娩后的身体恢复以及照顾新生儿。在西班牙,产假是所有女性员工的法定权利。
陪产假:
西班牙的陪产假属于“子女出生与照护津贴”(Nacimiento y Cuidado de Menor)的一部分,保障父母双方享有平等的家庭休假权利。
特殊情况的假期延长:
线上申请(使用数字证书或 Cl@ve 账户):
线上申请(无数字证书):
邮寄申请:
现场申请:
所需文件:
在西班牙,陪产假和产假的申请资格取决于多种因素,包括就业状态、社会保障缴费情况以及具体家庭状况。
在西班牙,试用期在固定期限合同和无固定期限合同中都较为常见。试用期允许雇主在提供正式或长期职位前,评估新员工是否适合该岗位。
在西班牙,终止劳动合同所需的通知期取决于合同类型(固定期限或无固定期限)以及员工的服务年限。
遣散费是员工在其劳动合同终止时可能获得的一种经济补偿。在西班牙,遣散费的规定因解雇的具体情况以及适用的法律法规而异。
西班牙的加班工资通常受国家劳动法和集体谈判协议的共同约束。以下是一些关键要点:
在西班牙,工伤由国家社会保障体系负责保障。若员工在工作中受伤,通常有权获得医疗治疗、康复服务以及经济补偿。
第一步:合作协议/MSA
第二步:岗位说明(采购订单)
第三步:雇佣协议/聘用函
第四步:入职流程
我们将向候选人提供以下文件以供签署:
在收到上述文件后,我们将为员工办理官方注册手续。
第五步:移民流程(如适用)
对于负责西班牙员工管理的全球人力资源团队来说,了解并遵守该国的家庭假期法律至关重要。以下是确保企业政策合法合规且具有竞争力的一些关键战略考量:
遵守当地法律:
竞争优势:
全球假期政策统一化:
持续审查与更新政策:
离职流程可分为以下四类:
在西班牙,对雇主提前解除固定期限劳动合同和无固定期限劳动合同有严格的规定。
固定期限合同:
在西班牙,雇主在合同到期前解除固定期限雇佣合同通常在特定条件下是允许的。但如果解除并非正当理由,雇主可能需要向员工支付赔偿金。
无固定期限合同:
在西班牙,雇主提前解除无固定期限劳动合同通常在特定条件下是允许的。然而,雇主必须有正当理由,且可能需要提前通知员工。
分享您的雇佣需求,获取定制化方案。